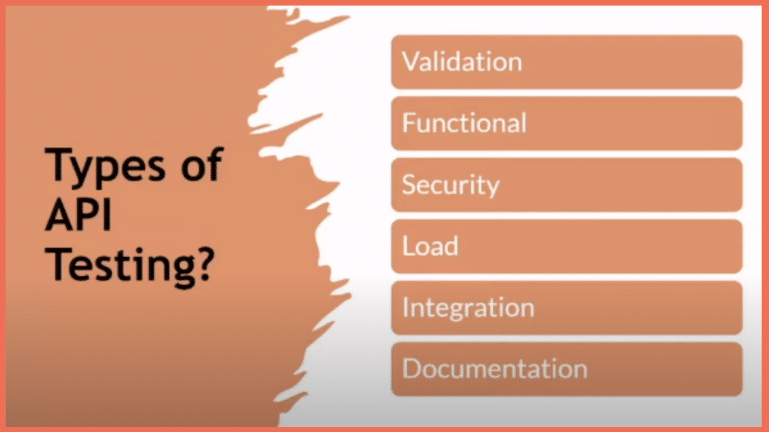
In the fast-paced field of cybersecurity, penetration testers, or pen testers, are playing an increasingly important role in society. The purpose of this blog is to provide prospective employees with an extensive professional road map for penetration testing. It goes over the essentials of this field, such as definition, duties, educational requirements, skills required, career advancement, and useful advice for landing a job. By the time you finish reading this essay, you will have a thorough understanding of the tools and procedures needed to start a lucrative penetration testing profession in 2024.
What is Penetration Testing?
An authorized simulated assault on a computer system is called a penetration test, or pen test, and it is done to assess the system’s security. To identify and illustrate the effects of system flaws on corporate operations, penetration testers employ the same instruments, strategies, and procedures as attackers. Typically, penetration testing mimic a range of potential threats to a company. They may assess a system’s resilience to assaults from a variety of system roles and from both authenticated and unauthenticated locations. A pen test may explore every facet of a system given the appropriate scope.
What advantages may penetration testing offer?
Software and systems should ideally have been created with the intention of removing harmful security issues from the beginning. An assessment of the success of that goal can be obtained by a pen test. Pen testing has benefits for an organization.
- Identify systemic vulnerabilities
- Assess the stability of the controls.
- Encourage adherence to data security and privacy laws (such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR).
- Give management examples, both quantitative and qualitative, of the existing security posture and budget priorities.
Because they can offer comprehensive information regarding security system flaws, penetration testers are highly helpful. They make it possible for businesses to identify security concerns and take preventative action to lessen the dangers. Pen testers help strengthen cybersecurity posture by providing in-depth analysis and practical suggestions that lower the likelihood of data breaches, monetary losses, and reputational harm.
Understanding Penetration Testing
Penetration testing is the rigorous process of reviewing and evaluating security mechanisms in computer networks, applications, and systems. It operates similarly to cyberattacks, employing a systematic approach to identify potential vulnerabilities that an attacker may exploit. This proactive strategy helps identify and fortify weaknesses before malicious actors take advantage of them.
Roles and Responsibilities of Penetration Testers:
Penetration testers, often known as ethical hackers (there is a difference though – read the difference between the two), conduct carefully thought-out, simulated attacks while keeping ethical considerations and express agreement in mind. Finding weak places in a company’s digital infrastructure is their primary duty. This means utilizing a range of testing methodologies, including black-box, white-box, and gray-box testing, to identify potential weak areas. Pen testers produce comprehensive reports and analyze their findings as well. These studies are immensely helpful resources for companies, providing in-depth analysis to fortify security protocols against cyberattacks and pinpoint possible new points of penetration.
The Significance of Pen Testing in Cybersecurity:
Organizations that want to bolster their cybersecurity defenses in the connected digital world must engage in penetration testing. Organizations that use a proactive strategy are able to identify vulnerabilities and address them prior to malicious actors exploiting them. Pen testers aggressively manage vulnerabilities and do comprehensive assessments to significantly enhance cybersecurity posture. By taking this proactive measure, an organization’s risk of future data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage is reduced.
Penetration testing is therefore a proactive approach to mitigate internet dangers. It is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities but also for enabling organizations to strengthen their defenses, lower risks, and provide a robust security posture against dynamic cyberattacks.
How to Become a Penetration Tester?
To become a penetration tester, or pen tester, one must follow several educational paths, take different courses, and obtain the necessary certifications and competences. Many individuals start this area without formal qualifications, however companies frequently favor applicants with bachelor’s or master’s degrees in cybersecurity, computer science, IT, or related subjects. However, earning relevant credentials and having the necessary abilities are still crucial for anybody aiming to become penetration testers.
Educational Requirements and Preferred Degrees
Candidates with degrees in cybersecurity, computer science, IT, or similar fields are usually sought after by employers. Formal degrees are not, however, required in order to pursue a profession in penetration testing. Many experts who were once involved in unethical hacking have made a successful transfer into this area without receiving any official schooling. The absence of a degree can be made up for by laying a solid basis through self-directed study, practical experience, and the acquisition of pertinent certifications.
Alternative Paths: Entering Penetration Testing Without a Degree
Without a degree, one can enter the penetration testing field by gaining real-world experience in network engineering, application programming with a security focus, or security administration. To enter the sector without requiring formal academic degrees, one might pursue self-learning projects, get applicable certifications, and develop a persuasive portfolio.
Essential Skills and Certifications for Pen Testers
Penetration testers need to have a wide variety of abilities, including technical know-how, the ability to solve problems, and a deep understanding of cybersecurity. Programming languages, threat modelling, network and application security, and security technologies are all crucial to understand. Acquiring professional credentials, like the Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) and Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP), is highly beneficial and oftentimes a prerequisite for work.
Furthermore, gaining real-world experience through projects, internships, or role-playing is a significant method to increase one’s level of competence in the field. A proficient penetration tester should also be able to use theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios and stay current with industry advancements.
The Penetration Tester Career Path
Becoming a penetration tester is a dynamic process that involves key phases centered around learning new material, honing existing skills, and obtaining practical experience. A solid understanding of security systems and information technology (IT) is necessary for this field of employment. Certification acquisition, skill development, and real-world experience are prioritized, and these may frequently be gained through competitive engagements or internships.
Understanding IT and Security Systems:
A penetration tester’s professional path requires a deep grasp of IT and security technologies. This entails being well-versed in network infrastructures, application architectures, security protocols, and operating systems. Acquiring this basic knowledge allows aspirational professionals to navigate the environment effectively while identifying and minimizing potential hazards.
Acquiring Relevant Skills and Certifications:
To succeed as a penetration tester, you must acquire a wide set of abilities. Proficiency in programming languages, threat modelling, network and application security, and a variety of security evaluation tools is necessary. Obtaining certifications from industry leaders like the Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP), Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), and Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) will further strengthen credentials and skills in this profession.
Gaining Practical Experience:
Theoretical understanding alone is insufficient; practical application is essential. Aspiring penetration testers usually hunt for internships or take part in Capture the Flag (CTF) events. These experiences enable users to apply their skills in simulated environments and gain awareness of a range of cybersecurity challenges through hands-on exposure to real-world circumstances.
Career Progression and Opportunities:
Opportunities for advancement beyond entry-level positions are provided via the penetration tester career path. With a mix of experience and skill, people can move up to senior roles or specialized professions in the cybersecurity sector. These careers might involve leading specialized testing teams, focusing on certain areas such as red teaming or threat intelligence, or transitioning into information security management.
Continuous Learning and Industry Trends:
In order to keep current with evolving industry trends and continue learning new things, one must always be studying in this sector. Because cybersecurity is a dynamic field, it requires flexibility, agility, and a constant awareness of emerging threats, tools, and tactics. For long-term success and progress in this industry, professional development and ongoing education are essential.
Salary Ranges and Job Market Demand:
The increasing threat environment that companies in a variety of industries must contend with has led to a strong need for skilled penetration testers. These experts’ pay ranges vary depending on their sector, region, experience, and credentials. The average base wage in the United States is around $119,554 annually as per Indeed. These numbers, however, are subject to large variation depending on personal qualities and local labor market conditions.
A diverse skill set that includes both technical aptitude and soft abilities is necessary to become a proficient penetration tester. Professionals may successfully discover, resolve, and explain security issues while upholding ethical standards thanks to this all-inclusive combo.
Technical Skills
Coding Proficiency: Proficiency in computer languages is essential for a penetration tester. Professionals with coding skills in languages like Python, Ruby, or PowerShell are able to create scripts, automate processes, and identify possible weaknesses in systems and apps. Penetration testers might use code to build bespoke tools or take use of known vulnerabilities for testing.
Network Security Expertise: It is essential to have a thorough grasp of network security concepts and procedures. This includes being aware of intrusion detection systems, firewalls, encryption methods, and network design. Network security expertise enables penetration testers to evaluate and strengthen network defenses, spot flaws, and stage attacks to reveal possible vulnerabilities.
System Analysis Skills: Penetration testers must be capable of doing in-depth system analysis. This entails analyzing operating systems, comprehending system setups, and evaluating implemented security measures. Their ability to analyze security controls, find vulnerabilities, and suggest workable repair plans is made possible by their system analysis capabilities.
Soft Skills
Problem-Solving Aptitude: The ability to solve problems well is essential for penetration testing success. These experts deal with intricate security issues and have to handle a variety of situations in order to find weaknesses. In this sector, the capacity to think critically, tackle issues methodically, and come up with creative solutions is crucial.
Communication Skills: Proficiency in communication is crucial for penetration testers in order to properly and concisely convey their results. Technical and non-technical stakeholders alike must be presented with technical knowledge in a consistent way by them. It is ensured via effective communication that vulnerabilities are known and dealt with quickly.
Ethical Integrity: Integrity and ethical behavior are non-negotiable in the penetration testing industry. Fundamental values that guide their work include upholding ethical norms, honoring boundaries, getting express consent before testing, and guaranteeing the confidentiality of sensitive data. Upholding ethical integrity cultivates professional connections by preserving trust with stakeholders and clients.
Critical Skills for Success
The most effective penetration testers combine technical know-how, analytical problem-solving skills, persuasive communication qualities, and a dedication to moral behavior. Their ability to dig deeply into systems, networks, and applications to find vulnerabilities is made possible by their technical talents. The ability to solve problems enables original thinking and inventive solutions to security problems. By ensuring that their results are comprehended and applicable, effective communication improves the security posture of the company. Credibility and trust are maintained by ethical integrity, which is necessary for long-term success in this fast-paced industry.
Learning Penetration Testing
Learning penetration testing in the ever-changing field of cybersecurity requires making use of a variety of resources, obtaining real-world experience, and keeping up with changing trends. This comprehensive strategy guarantees that experts have the most recent information and abilities to successfully tackle new dangers.
Resources for Learning
Online Courses and Workshops: Anyone who is interested in learning penetration testing may take advantage of a variety of online workshops and courses. These materials address a wide range of subjects, including as exploit creation, network security, vulnerability assessment, and ethical hacking. Thrive EdSchool has a detailed course on web security testing that covers penetration testing for beginners and advanced learners.
Books and Educational Materials: Apart from digital media, books are also important sources of deep information. Comprehensive insights into the area may be obtained via publications that address penetration testing, cybersecurity concepts, and particular tools and methodologies. Advanced approaches and up-to-date knowledge may be found in educational resources including whitepapers, research papers, and documentation from cybersecurity conferences.
Practical Tips for Real-World Experience
Competitions and Capture The Flag Events: Engaging in contests and CTF activities offers practical exposure to simulated cybersecurity situations. These simulations of actual cyberthreats provide participants the chance to work through problems, spot weaknesses, and put their practical knowledge to use in a safe setting. They encourage the kind of creativity, problem-solving, and collaboration that are necessary for a successful penetration testing career.
Contributing to Open-Source Projects: Participating in open-source cybersecurity initiatives provides exposure to real-world problems and real-world experience. Working together with international communities on security-related initiatives allows people to address current cybersecurity concerns while making a contribution, learning from peers, and improving their skills.
Internships and Entry-Level Positions: Taking up internships or entry-level positions in IT departments or cybersecurity companies exposes one to business procedures directly. These jobs provide people the chance to put their theoretical knowledge to use in actual situations, learn about organizational security frameworks, and comprehend the effects of security measures on the real world.
Staying Updated with Cybersecurity Trends
Continuous Learning: The field of cybersecurity is dynamic, as cyber threats are ever-changing. It is essential to keep up with the most recent methods, strategies, and trends employed by cybercriminals. Professionals may do this by attending webinars, attending conferences and seminars in the sector, subscribing to reliable cybersecurity blogs, and engaging in ongoing learning.
Adapting to Emerging Threats: Penetration testers can predict possible dangers and create efficient security plans by having a thorough understanding of emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and attack routes. In order to efficiently react to and mitigate evolving risks, it entails investigating emerging technologies, threat intelligence platforms, and performing research.
Landing a Job as a Penetration Tester
Making a lasting impression with your portfolio and CV, networking with industry people, and doing well in interviews are all essential to landing a penetration testing position. This is a condensed manual that is enhanced with extra information and is based on professional advice:
Crafting an Impactful Resume and Portfolio:
- Highlight your experience with penetration testing and related talents, with a focus on practical knowledge of finding and fixing vulnerabilities.
- Provide thorough justifications for every step of your work, demonstrating your proficiency in running several kinds of tests, such as white-box, gray-box, and black-box tests.
- Emphasize your experience with penetration testing tools like Metasploit or Burp Suite, as well as your qualifications and specialized training. Examples of these include Certified Ethical Hacker, Offensive Security Certified Professional, and more.
- Highlight your contributions to independent research, bug bounty schemes, or open-source security initiatives to show that you are a proactive participant and that your talents are being used in the real world.
Building Networks and Leveraging Connections:
- Become involved in cybersecurity networks and forums to network with experts in the field, take part in debates, and share your knowledge of new developments in the field.
- Participate at conferences, webinars, and industry events to network with peers, industry experts, and possible employers.
- Make use of social media sites such as LinkedIn to network, exchange insightful articles, participate in conversations, and position oneself as an authority in the industry.
Job Interview Strategies for Standing Out:
- Display your technical prowess by talking about prior experiences, outlining how you’ve handled certain security issues, and showcasing your mastery of different penetration testing techniques.
- Demonstrate your proficiency with penetration testing tools and procedures by providing specific examples of how you have utilized them to find vulnerabilities and fortify security measures.
- Emphasize experience in testing, creating thorough reports outlining vulnerabilities found, and offering practical security suggestions based on an organization’s requirements.
- During interviews, show that you are interested in the company’s security procedures, are aware of its particular difficulties, and can explain how you might help them achieve their security goals by asking thoughtful questions.
Following these comprehensive guidelines enhances the chances of not only landing a penetration testing role but also establishing a successful career in the dynamic and vital field of cybersecurity.
Conclusion
In 2024, a profession as a penetration tester will demand schooling, real-world experience, fundamental abilities, and ongoing education. Aspiring people may use this handbook to equip themselves with the information and tools needed to enter the fast-paced world of cybersecurity. Securing qualifications, real-world experience, networking opportunities, and readily available information can help one embark on a prosperous professional path in penetration testing.