API (Application Programming Interface) testing is a crucial skill for software professionals. Whether new to testing or an experienced pro, this blog is your go-to resource.
We’ve distilled valuable insights from The Test Tribe’s 4th Virtual Meetup on API Testing with Pricilia into an easy-to-understand blog guide. You can watch the complete video below for the visual learner’s out there.
Table of Contents
What is an API?
API is an acronym that stands for application programming interface. API is a set of routines, protocols, and tools for building Software Applications. APIs specify how one software program should interact with other software programs. Typically, API facilitates the reusability.
For example:
If a user needs to book a room in Hyatt Regency. The user can directly do it on Hyatt Regency website, or through travel booking websites like MakeMyTrip, Trivago, etc.. So, here, the Hyatt Regency develops an API and provides specific(read/write) access to travel agencies through which users can view/book their hotels.
Common Types of API

Various APIs have distinct purposes, each with advantages and drawbacks. The most prevalent API categories include:
Open API (Public API):
These APIs are accessible to all developers and users. They typically have minimal authentication and authorization measures and may limit the data they provide. Some open APIs are free, while others require a subscription fee based on usage.
Private API (Internal API):
Private APIs remain inaccessible to the general public and are intended solely for internal use within an organization. They often employ stricter authentication and authorization protocols, granting access to an organization’s internal data and systems to its employees or trusted partners.
Partner API:
Partner APIs are shared exclusively between strategic business partners. These APIs are not open to the general public and require specific permissions for access. They facilitate business-to-business activities, often involving the exchange of sensitive data, and typically employ robust authentication, authorization, and security measures.
Understanding the Client-Server Architecture
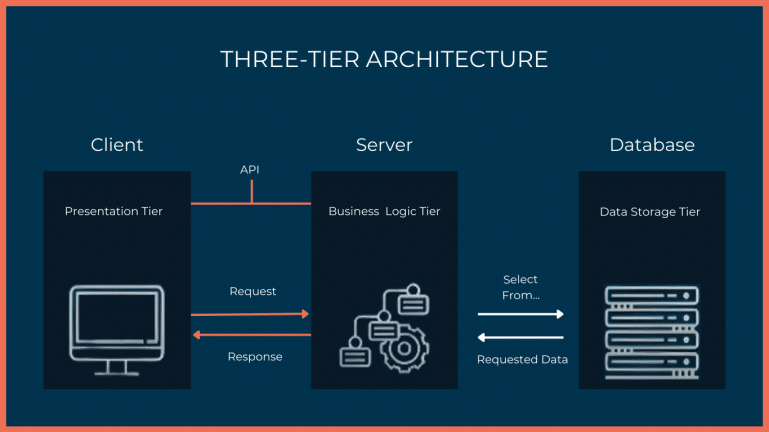
Client-server architecture in API testing, within the context of a three-tier architecture, involves the interaction between different components for efficient and organized testing. Here’s an overview of this concept:
1. Presentation Tier (Client):
- In API testing, the client or presentation tier represents the front-end or user interface through which users interact with an application.
- Testers may simulate user actions and interactions with the client interface, such as making HTTP requests to the API endpoints.
- The focus is ensuring the client can effectively communicate with the API and process the responses.
2. Application Tier (Server):
- In API testing, the API resides in the server or application tier.
- This tier handles incoming client requests, processes them, and provides responses.
- Testers conduct various API tests here, including functional testing to validate the API’s behavior, performance testing to assess its responsiveness under load, and security testing to identify vulnerabilities.
3. Data Tier (Database):
- In a three-tier architecture, the data tier, or database, stores and manages the application’s data.
- While API testing primarily focuses on the interaction between the client and server, verifying that the API correctly accesses and manipulates data in the database is essential.
- Testers may perform database-related tests like data integrity checks and consistency validation.
What is API Testing?
API testing is a critical process in software testing that focuses on evaluating the functionality, performance, and reliability of an Application Programming Interface (API). Incorporating snapshot testing can further enhance the accuracy of your API tests. Understanding why API testing is important can enhance your approach to evaluating APIs. It involves testing the API’s endpoints, request-response mechanisms, and data exchanges.
Steps Involved: Process Used in API Testing

Here’s a detailed explanation of the API testing process outlined:
1. Review and Understanding of API Specifications
Begin by thoroughly reviewing the API documentation and specifications. This step ensures that testers clearly understand what the API is designed to do, its endpoints, input parameters, and expected output.
2. Categorize Entities Based on Flow
Categorize the various entities, such as endpoints, methods, and data flows, based on the API’s functionality. This categorization helps in organizing test scenarios effectively.
3. Define the Parameters
Identify and define the parameters required for each API endpoint. Parameters include inputs, headers, query parameters, and authentication details. Ensure that you understand the purpose of each parameter.
4. Learn How to Send Requests for Different Endpoints
Familiarize yourself with the tools and methods for sending requests to the API endpoints. This may involve API testing tools, command-line tools, or scripting in a programming language.
5. Frame the Test Cases
Create comprehensive test cases for each API endpoint. Test cases should cover various scenarios, including valid and invalid inputs, boundaries, and edge cases. Define the expected outcomes for each test case.
6. Add Assertions on the Expected Results
Define assertions to validate the API responses. Assertions are criteria that must be met for a test case to pass. They can include checking response status codes, data integrity, and expected values.
7. Test Execution
Execute the test cases against the API endpoints. Ensure that you follow a systematic approach, covering all defined scenarios. This phase involves sending requests, receiving responses, and comparing the actual outcomes to the expected results.
8. Report the Failure
If a test case fails, document the failure with as much detail as possible. Include information about the test environment, input data, and any error messages or unexpected behavior encountered during testing.
Why is API Testing Done?

In the ever-evolving realm of software development, ensuring the reliability and efficiency of applications has never been more crucial. This is where API testing steps into the spotlight as a game-changer. In this, we explore why API testing should be integral to your testing strategy.
1. Time Efficiency
First and foremost, API testing is a time-saver. Traditional testing methods often involve testing the entire application, which can be time-consuming, especially in complex systems. API testing, on the other hand, allows testers to focus on specific functionalities or endpoints. This targeted approach significantly reduces testing time, allowing quicker development cycles and faster time-to-market.
2. Cost Reduction
In the world of software development, time is money. You’re effectively reducing testing costs by accelerating the testing process and streamlining it with API testing. With fewer resources required for testing, your organization can allocate resources more efficiently and effectively, ultimately saving valuable budgetary resources.
3. Language Independence
API testing breaks down language barriers. API testing is language-independent, unlike some testing methods that depend on specific programming languages or technologies. This means you can test APIs built with different technologies or languages without a deep understanding of each language. This flexibility is a significant advantage in today’s multilingual software landscape.
4. Core Functionality Testing
At the heart of every software application lies its core functionality. API testing specializes in scrutinizing this essential aspect. It allows you to dive deep into the core of your application, testing how its various components interact and ensuring that they perform as expected. This pinpoint accuracy in testing core functions enhances the overall quality of your software.
5. Risk Mitigation
Software development inherently carries risks. API testing acts as a risk mitigation tool. By thoroughly testing APIs before integrating them into the application, you can identify and address potential issues and vulnerabilities early in the development cycle. This proactive approach reduces the likelihood of critical failures in the production environment, safeguarding your system’s integrity.
Types of API Testing
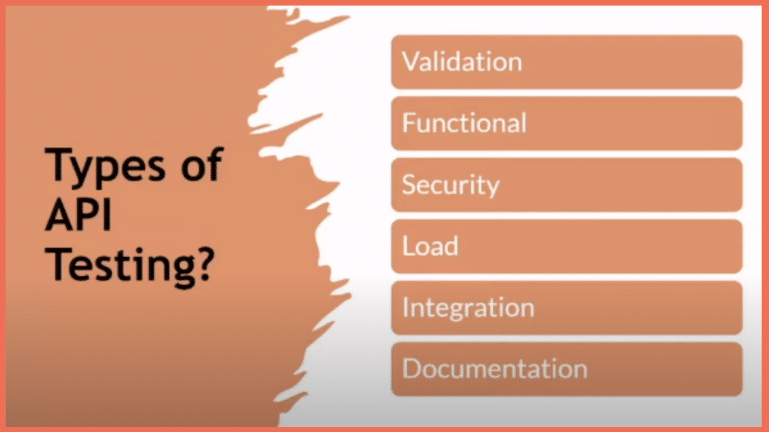
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are the backbone of modern software, enabling seamless communication between applications and services. To ensure that APIs perform flawlessly and securely, API testing comes into play. Let’s take a closer look at the various types of API testing and their distinct roles in the software testing ecosystem.
1. Validational API Testing
Validational API testing, or Schema Testing, verifies that the API responses adhere to the expected data format and structure. This type of testing ensures that the data exchanged between the API and the application is correctly formatted, preventing potential data-related issues.
2. Functional API Testing
Functional API testing is all about functionality. It verifies whether the API functions as intended by testing its various endpoints and methods. Testers create test cases to assess the API’s behavior, input validation, and output correctness. This type of testing is critical for confirming that the API delivers the expected results under various scenarios.
3. Security API Testing
In an age where cybersecurity is paramount, Security API Testing is indispensable. It involves scrutinizing the API for vulnerabilities and security flaws. This testing type assesses the API’s ability to protect sensitive data, prevent unauthorized access, and resist common security threats like SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
4. Load API Testing
Load API testing assesses how well the API performs under different load and stress levels. It helps determine the API’s capacity to handle concurrent requests and large volumes of data. Testers can identify performance bottlenecks by simulating heavy loads and ensuring the API remains responsive and reliable in real-world scenarios.
5. Integration API Testing
Integration API testing evaluates how well the API interacts with other systems and services within an application’s ecosystem. It ensures seamless communication between various components, detecting integration issues that could disrupt the application’s overall functionality.
6. Documentation API Testing
API documentation is the user manual for developers and users interacting with your API. Documentation API testing validates that the documentation accurately represents the API’s behavior. It confirms that developers can rely on the documentation to understand how to use the API effectively.
Common Types of API Protocols
API protocols form the foundation for exchanging and communicating data between software systems. Two prominent protocols in web services and APIs stand out: SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) and REST (Representational State Transfer). Let’s delve into each of these protocols to understand their key characteristics and use cases:
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol):
- SOAP is a protocol for exchanging structured information in web services using XML.
- It relies on a predefined set of rules for message formatting and communication.
- Known for its strict standards and support for complex operations, it’s commonly used in enterprise-level applications.
REST (Representational State Transfer):
- REST is an architectural style for designing networked applications.
- It uses standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) and operates on resources represented as URLs.
- Known for its simplicity and flexibility, it’s widely used for web APIs, including web and mobile applications.
HTTPS Methods You Need to Know About
When interacting with web APIs, understanding the core HTTP methods is crucial. Let’s dive into the essential HTTP methods you need to know for seamless communication with APIs:
GET:
- This method is all about retrieval. It requests data from a specified resource.
- It’s commonly used for fetching information from a server without changing the resource.
POST:
- POST is all about submission. It sends data to be processed to a specified resource.
- This method is often used when creating a new resource or submitting form data to a server.
PUT:
- PUT is for updating. It sends data to a specific resource to replace or update it.
- Use PUT when you want to modify an existing resource entirely, making it a powerful update tool.
DELETE:
- DELETE is the method for well deleting a specified resource.
- It removes a resource from the server, providing a meaningful way to manage data.
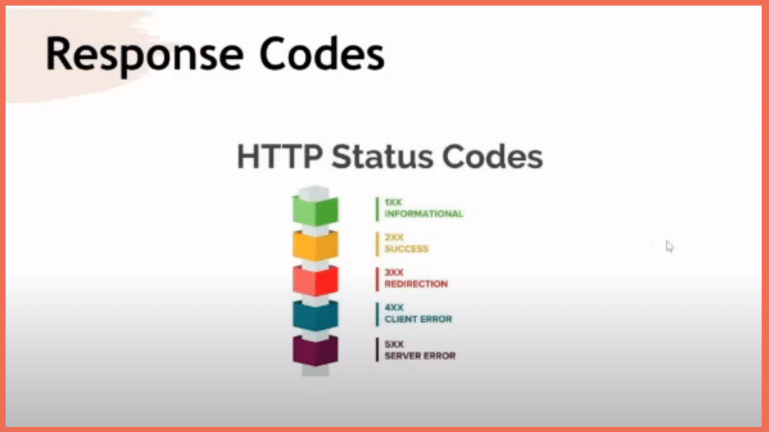
Response Codes in API Testing
In API testing, understanding response codes is akin to reading the language of the digital realm. Here’s a concise guide to the response codes you’ll frequently encounter:
1XX – Informational:
- These codes provide information about the status of ongoing requests. A comprehensive Postman status code list can be found here.
- Typically, they signal that the request is received and understood, but further action may be required.
2XX – Successful:
- The coveted 2XX codes signify successful request processing.
- A 200 OK, for instance, indicates that the request was processed without issues, delivering the expected results.
3XX – Redirection:
- These codes indicate the client must take additional steps to complete the request.
- The 301 Moved Permanently is commonly seen, which redirects the client to a new URL.
4XX – Client Errors:
- These codes come into play when something goes amiss on the client side.
- A 404 Not Found, for instance, means the requested resource couldn’t be located on the server.
5XX – Server Errors:
- Server errors signal that something has gone awry on the server’s end.
- A 500 Internal Server Error is a catch-all for various server-related issues.
Best Practices to Follow When Testing APIs
API testing is a vital component of software quality assurance. Following best practices is crucial to ensure robust and reliable APIs. Here, we explore six key practices:
- Call Sequencing: After standalone validation, consider the sequencing of API calls. Ensure that APIs interact seamlessly, maintaining data integrity and functionality.
- Parameterization: Implement parameterization to test various inputs and scenarios, uncover potential issues, and ensure your API can handle diverse data.
- Delete Operation Handling: Consider how your API handles delete operations. Ensure it behaves as expected and that data deletion is secure and controlled.
- Scenario-Based Grouping: Organize your API requests based on scenarios. This makes testing more systematic, helping you identify and address specific use-case issues.
- Automation: Whenever possible, automate your API tests. Automation streamlines testing detects issues early and accelerates the testing process.
- CI/CD Integration: Integrate API testing into your CI/CD pipeline. This ensures continuous testing, reducing the likelihood of bugs slipping through production.
Real-Time Challenges in API Testing
API testing brings its own set of real-time challenges. Here’s a quick overview of these hurdles and how to tackle them:
- Initial Setup: Setting up API testing environments can be complex. Streamline this by using containerization tools like Docker for consistent setups.
- Documentation: Inadequate or unclear API documentation can slow testing. Collaborate closely with developers to ensure comprehensive documentation.
- Without User Interface: APIs lack user interfaces, making testing less intuitive. Leverage API testing tools and scripts to interact with APIs directly.
- Tool Selection: Choosing the proper testing tools is critical. Assess your project’s needs and opt for tools that align with your testing objectives.
- Error Handling: Robust error handling is essential. Test various error scenarios to ensure your API gracefully handles unexpected situations.
- Drafting Scenarios: Creating practical test scenarios requires careful planning. Understand the API’s functionality and potential use cases to draft meaningful scenarios.
- Coding Skills: Some testing tools may require coding skills. Invest in training or consider user-friendly tools to accommodate testers with various skill levels.
What to Learn Next?
The next part of this blog (and the workshop had a live demonstration) is found in the Postman tutorial blog. Here you will learn how to do API testing using Postman.
Check related learning courses:
We recreated this blog using the content from Pricilla Bilavendran‘s API Testing Workshop at The Test Tribe’s 4th Virtual meetup. Pricilla is a Postman Supernova and a long-time contributor to the testing community. She is also an instructor for the Postman course that helps you learn API Testing on our learning platform, Thrive EdSchool. If you are looking for a solid resource to master the Postman tool for API testing, we urge you to check it out. You can connect with her on social media by following the links below.





2 thoughts on “API Testing Tutorial for Complete Beginners”
Great tutorial! This guide breaks down API testing in a way that’s easy for beginners to follow and understand. The examples and step-by-step explanations make it much clearer. Appreciate the insights on tools and best practices as well—super helpful for anyone just starting in API testing!